How does it work?
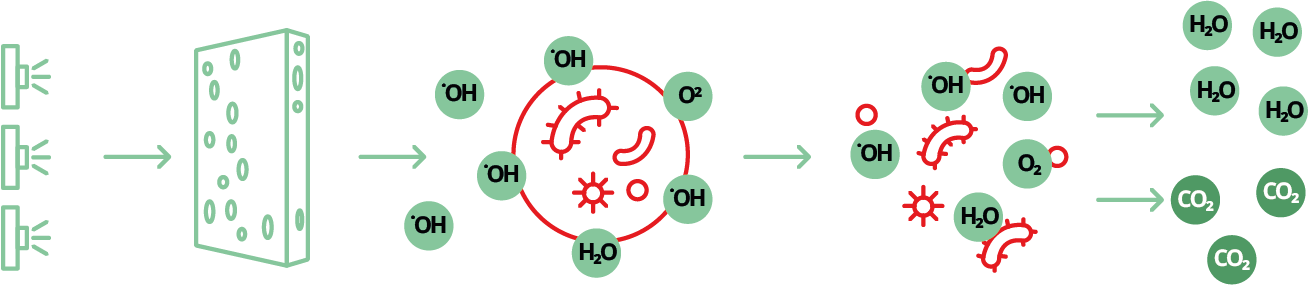
Photocatalysis (PCO) is a technology that has been developed for over 50 years, using light and nanomaterials such as titanium dioxide (TiO2), to oxidise pathogens and break down volatile organic compounds (VOCs) into harmless substances such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). This process completely eliminates contaminants and does not require filter replacement, reducing costs and increasing efficiency. It ensures a safe growing environment even at higher air humidity, minimising the risk of mould and pathogen growth.
A porous ceramic layer coated with TiO2 nanoparticles is irradiated with selective UV light. Active oxygen forms generated on the surface of the photocatalytic layer enable the degradation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), the conversion of inorganic compounds into safe substances, and the inactivation of microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, mould and fungi).


