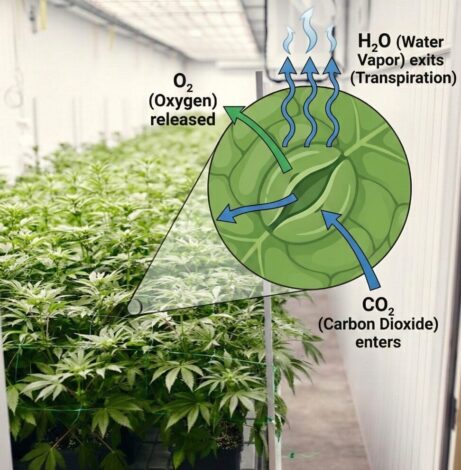
What is VPD and why is it so important?
VPD (Vapor Pressure Deficit) is the difference between the maximum amount of water vapour that air can hold at a given temperature (saturation pressure) and the actual amount of water vapour in the air. In practice, low VPD means very humid, ‘low-absorbent’ air, while high VPD means dry air that ‘draws’ water from the leaves. It is not relative humidity (RH) itself, but VPD that determines how intensively a plant absorbs water and then releases it into the environment.
Under controlled conditions (lighting, CO2, fertigation, HVACD), it is VPD that binds the entire physiological system of the plant together.
Transpiration (transport of water and nutrients) creates negative pressure in the xylem, which transports water from the roots, transfers macro- and microelements, and enables leaf cooling.


